Appearance
When placing multiple shapes or parts in a single view adjusting the appearance is helpful to highlight different areas or to represent real world visualization.
The color attribute sets the color of the shape displayed. The color parser will accept any of the following formats:
- A SVG color name
- A "hex" formatted color, eg
#RRGGBB(including optional alpha channels) - A tuple of
(R,G,B)values from 0 to 255 - CSS style
hsl(hue, % saturation, % lightnes) - CSS style
rgb()andrgba()arguments.
The transparency is can also be set from 0 to 1 with 1 being fully transparent and 0.5 being 50% transparent.
Use display = False to prevent a node from being shown on the viewer and exported models.
Note: Visual information like colors is only used if defined on the "root" shape or children of a
Partdeclaration.
Descriptions
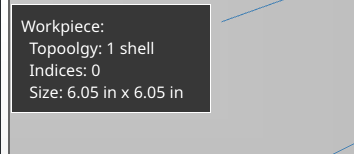
Each shape declaration has name and description attributes. These can be used to supply information to the popup in the viewer when an item is selected.
For example
# ...
Workpiece: workpiece:
color = '#222'
width = 6.05
height = 6.05
description = f"Size: {width} in x {height} in"
Will show a popup like this when clicked:
Material
The material can be set to an OpenCASCADE material name or a Material instance. The material name sets several properties such as how reflective the shape is. The Material instance is still under development but is planned to make all of these properties editable.
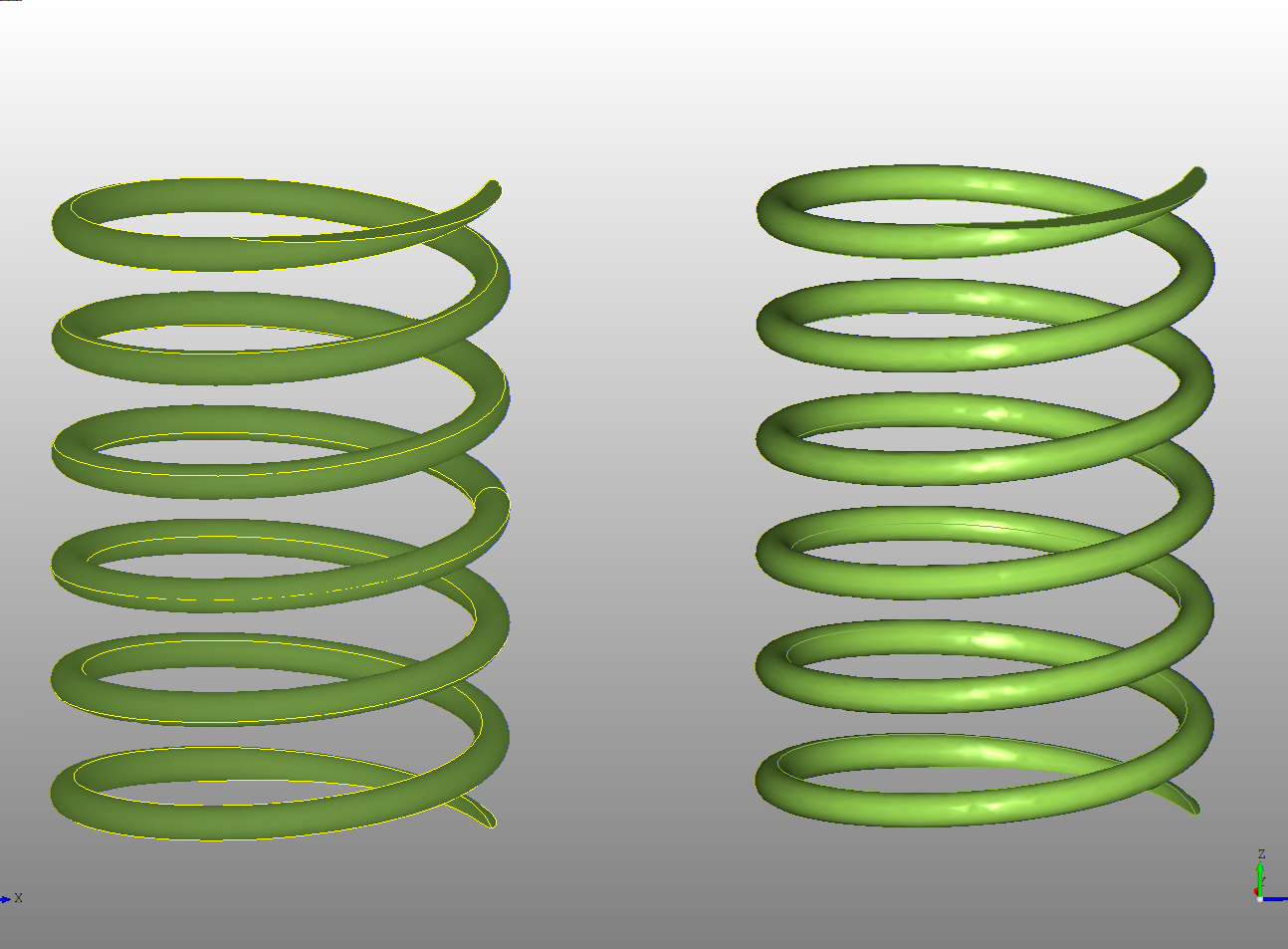
The material can be combined with a color for example this spring is using the same color with one set to "plastic" and the other set to "steel"
The following materials are currently:
| Material Name |
|---|
| aluminium |
| brass |
| bronze |
| charcoal |
| chrome |
| copper |
| default |
| diamond |
| glass |
| gold |
| jade |
| metalized |
| neon_gnc |
| neon_phc |
| obsidian |
| pewter |
| plaster |
| plastic |
| satin |
| shiny_plastic |
| silver |
| steel |
| stone |
| transparent |
| water |
Note: These can be retrieved by importing
from declaracad.occ.materials import MATERIALS
Physically based rendering
Opencascade 7.5.0 supports physically based rendering. DeclaraCAD now adds support for defining these parameters.
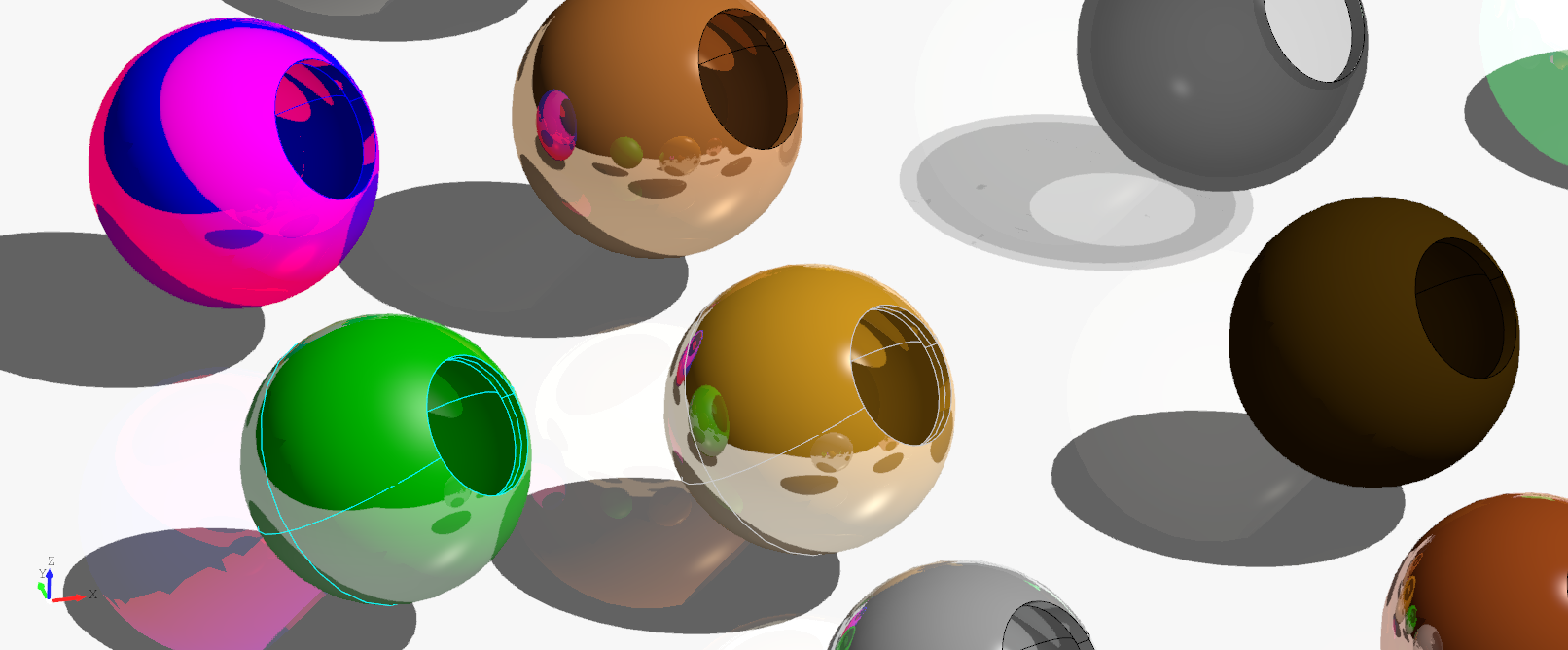

Note: The shadows, reflections, and raytracing viewer options must be enabled for these to materials properties to be rendered.
For example:
from declaracad.occ.api import *
from declaracad.occ.materials import Material, PBRMaterial, Fresnel
enamldef Ball(Part): part:
Cut:
color = part.color
material = part.material
Sphere: outer:
radius = 10
Sphere: inner:
radius = outer.radius-1
Cylinder:
radius = 5
height = outer.radius
enamldef Assembly(Part):
Plane:
color = 'white'
position = (0, 0, -14)
bounds = [(-80, -80), (200, 200)]
Ball:
position = (-30, 80)
direction = (-1, 1, 1)
color = 'blue'
material = Material(
name='custom',
specular_color='red',
shininess = 0.001,
pbr=PBRMaterial(
le=(0.5, 0.95, 0.9),
coat=Fresnel(model='dielectric', params=1.62),
base=Fresnel(model='constant', params=1),
)
)
Face colors
At the moment DeclaraCAD doesn't have a way to specify face colors on a shape, however there is a way to easily achieve this is to using the TopoShape node. Assign the face from the topology you want to color to the shape attribute of and add a material / color.
For example
Looper:
iterable = (2, 6, 10)
TopoShape:
material = 'chrome'
shape = arbor.topology.faces[loop.item]
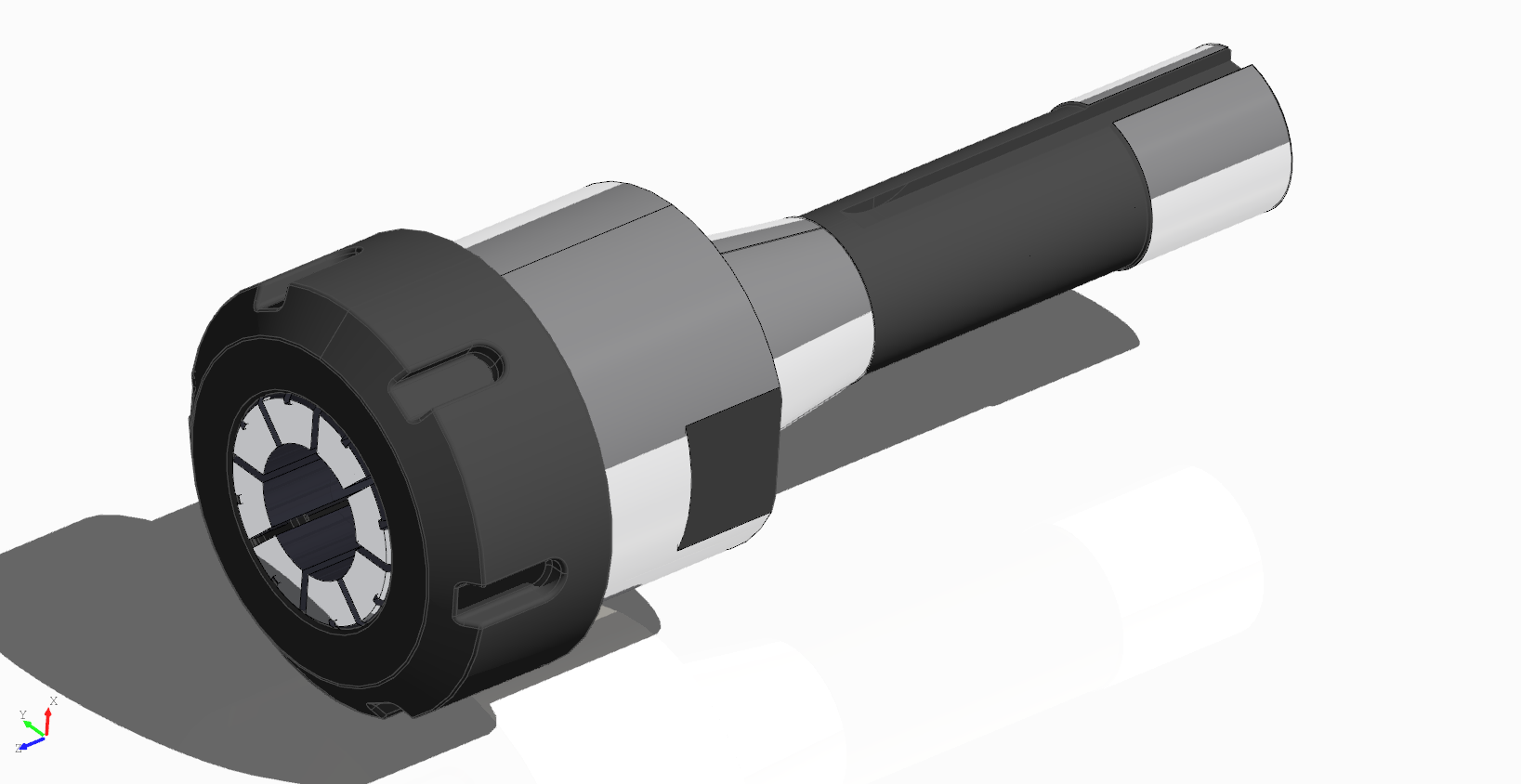
Note: These must be placed after the original shape so it is drawn on top of the existing face.
